Infrared thermometers swiftly and safely measure temperature without physical contact‚ utilizing infrared energy emitted by objects․
These devices are invaluable for diverse applications‚ ranging from medical diagnostics to industrial maintenance‚ offering convenience and hygiene․
Understanding their operation and safety features‚ as detailed in the instruction manual PDF‚ is crucial for accurate readings․
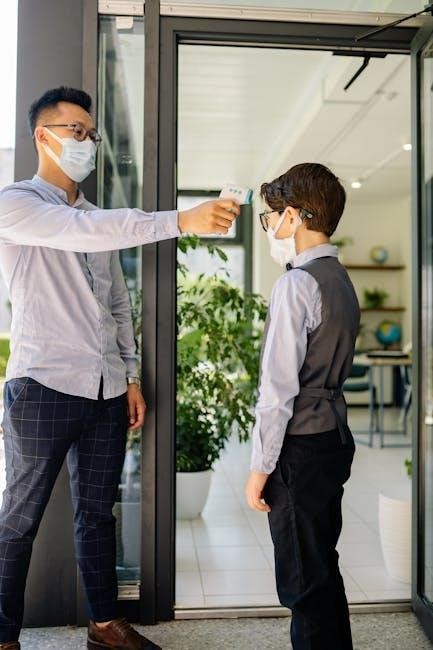

What is an Infrared Thermometer?
An infrared thermometer is a non-contact temperature measurement device‚ differing significantly from traditional thermometers; Instead of relying on physical contact‚ it detects and analyzes infrared energy radiated by an object to determine its surface temperature․ This technology makes it ideal for situations where contact is impractical‚ unsanitary‚ or dangerous․
As outlined in most infrared thermometer instruction manual PDFs‚ these devices are comprised of a lens to focus the infrared energy‚ a detector to convert the energy into an electrical signal‚ and a display to show the temperature reading․ They are commonly used in medical settings – like forehead and ear thermometers – and industrial applications for monitoring equipment and processes․
The instruction manual PDF will detail specific models‚ emphasizing that accuracy depends on factors like emissivity settings and distance to the target․ Understanding these nuances‚ as explained in the manual‚ is vital for obtaining reliable temperature measurements․
How Infrared Thermometers Work
Infrared thermometers function by detecting the infrared energy emitted by all objects – the amount of which increases with temperature․ As detailed in a typical infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF‚ the device doesn’t measure temperature directly‚ but rather the infrared radiation․
This radiation is focused by a lens onto a thermopile detector‚ which converts the energy into an electrical signal․ The signal is then processed by internal circuitry and displayed as a temperature reading․ Crucially‚ the instruction manual PDF will explain the importance of ‘emissivity’ – a material’s ability to radiate infrared energy – and how to adjust the thermometer accordingly for accurate results․
Factors like distance and ambient temperature also influence readings‚ and the manual provides guidance on optimal usage․ Understanding these principles‚ as outlined in the instruction manual PDF‚ ensures reliable and precise temperature measurements․
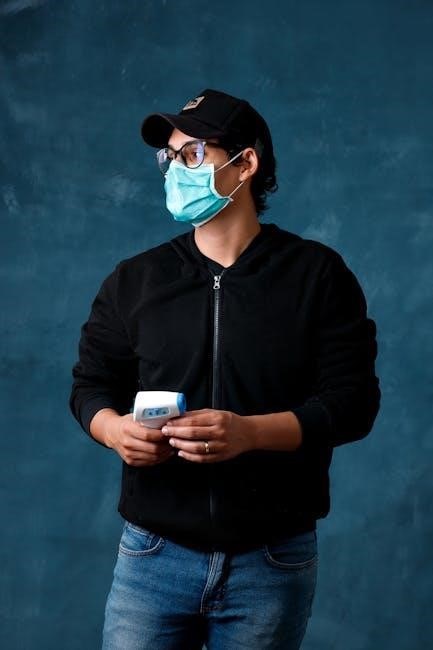

Types of Infrared Thermometers
Infrared thermometers come in various forms – forehead‚ ear‚ and industrial – each suited for specific applications․
Consulting the instruction manual PDF clarifies the best type for your needs and proper usage techniques․
Forehead Thermometers
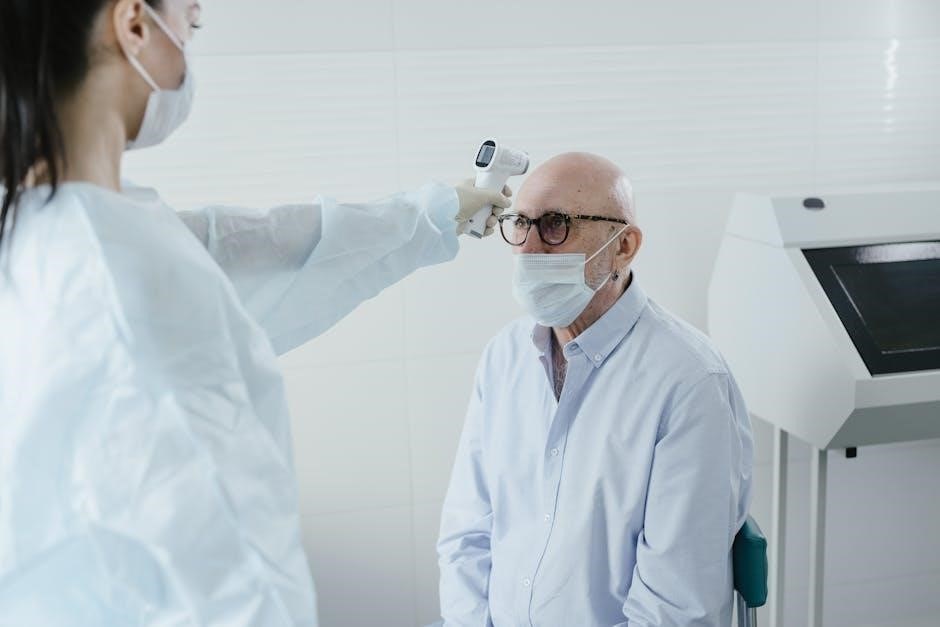
Forehead thermometers‚ also known as temporal artery thermometers‚ are widely used for quick‚ non-invasive temperature screening․ The instruction manual PDF emphasizes maintaining a stable distance – typically within one to five centimeters – for accurate readings․
These devices measure infrared radiation emitted by the temporal artery‚ located on the forehead․ Proper technique‚ as outlined in the manual‚ involves slowly scanning the thermometer across the forehead‚ avoiding hair or obstructions․
The manual will detail how to interpret the display‚ noting features like fever indicators and memory functions․ It also stresses the importance of cleaning the thermometer’s sensor after each use with a soft‚ dry cloth‚ as detailed in the safety section of the instruction manual PDF․
Understanding environmental factors‚ such as ambient temperature and direct sunlight‚ and their potential impact on accuracy is also covered within the manual’s guidelines․
Ear Thermometers
Ear thermometers‚ or tympanic thermometers‚ measure infrared heat waves emitted from the eardrum․ The instruction manual PDF stresses the importance of proper insertion technique for accurate results․ Gently pull the ear back and upward (adults) or downward (children) to straighten the ear canal before inserting the probe․
The manual details how to securely place the thermometer tip into the ear canal‚ ensuring a tight seal to prevent ambient noise from interfering with the reading․ A beep typically indicates a successful measurement․
The instruction manual PDF will also cover probe cover usage – essential for hygiene and accuracy – and proper storage․ It highlights potential error sources‚ like earwax buildup or incorrect positioning‚ and troubleshooting steps․
Always consult the manual for specific cleaning instructions and warnings regarding contraindications‚ such as recent ear surgery or infections․
Non-Contact Industrial Thermometers
Non-contact industrial thermometers are designed for measuring the surface temperature of objects from a distance‚ crucial for safety and efficiency in manufacturing‚ maintenance‚ and automotive applications․ The instruction manual PDF emphasizes understanding the distance-to-spot ratio – the area being measured relative to the distance from the thermometer․
It details how to adjust emissivity settings‚ a material property affecting infrared radiation‚ for accurate readings on various surfaces․ The manual will explain how to interpret readings‚ considering factors like surface reflectivity and ambient temperature․
Safety warnings within the instruction manual PDF highlight potential hazards when measuring extremely hot surfaces or moving machinery․ Proper aiming and understanding the laser sighting (if equipped) are critical․
Regular calibration‚ as outlined in the manual‚ ensures continued accuracy and reliability of the instrument․
Safety Information & Warnings
Carefully review the instruction manual PDF before use; it details crucial safety precautions‚ laser warnings (if applicable)‚ and electrical shock prevention measures․
Prioritize safe operation!

General Safety Precautions
Always consult the infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF for comprehensive safety guidelines before operating the device․ Ensure the thermometer is used within its specified operating conditions‚ avoiding extreme temperatures or humidity․
Do not attempt to disassemble or modify the thermometer‚ as this could result in malfunction or injury․ Keep the lens clean and free from obstructions to ensure accurate readings; use a soft cloth for cleaning․
Avoid pointing the thermometer at eyes or directly at highly reflective surfaces․ This device is intended for non-invasive temperature measurement only and should not be used for self-diagnosis or treatment․ Store the thermometer in a safe‚ dry place‚ away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures․ Regularly check the battery compartment for corrosion and replace batteries as needed‚ following the manual’s instructions․
Be mindful of potential hazards when measuring temperatures of moving objects or hazardous materials․
Laser Safety (If Applicable)
Refer to the infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF to determine if your model utilizes a laser sighting mechanism․ If present‚ the laser is a Class 2 or Class 3R laser product – never look directly into the laser beam․
Direct exposure to the laser beam can cause eye damage․ Avoid pointing the laser at people or animals․ Do not attempt to disassemble or modify the laser components․ The laser is intended solely for aiming the infrared sensor; it does not provide temperature readings itself․
Ensure the laser is switched off when not in use․ Be aware of potential reflections from shiny surfaces․ Follow all safety warnings and precautions outlined in the manual regarding laser operation․ If the laser appears damaged‚ discontinue use immediately and consult the manufacturer․ Proper laser safety practices are essential for preventing accidental eye injury․

Electrical Shock Hazards
Consult the infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF for specific electrical safety guidelines․ While most infrared thermometers are battery-operated and present a low electrical shock risk‚ certain models‚ particularly larger industrial units‚ may utilize external power sources․
Never operate the thermometer with damaged power cords or connectors․ Avoid using the device in wet or damp environments‚ as this increases the risk of electrical shock․ Do not attempt to disassemble or repair the thermometer yourself; internal components may carry hazardous voltages․
Always ensure the device is properly grounded if required․ Regularly inspect the battery compartment for corrosion or damage․ If you suspect an electrical fault‚ discontinue use immediately and contact a qualified technician․ Following these precautions‚ detailed in the manual‚ minimizes potential electrical hazards․
Understanding the Thermometer Components
Refer to the infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF to identify each part‚ including the display‚ buttons‚ and battery compartment․
Familiarity with these components ensures proper operation and accurate temperature readings․
Display Screen & Indicators
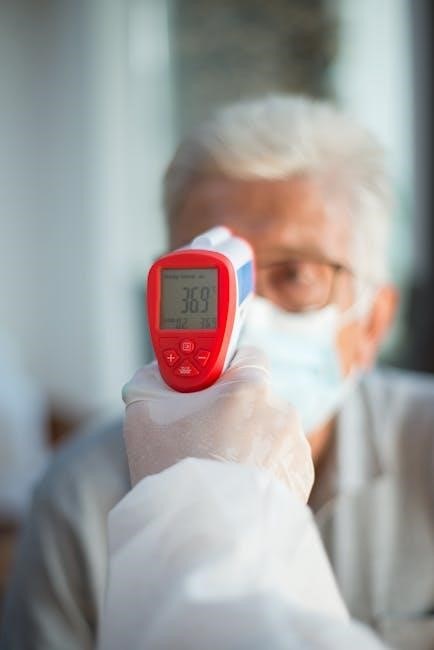
The display screen‚ as detailed in your infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF‚ is the primary interface for viewing temperature readings and device status․
Typically‚ it’s a digital LCD showing the measured temperature in either Celsius or Fahrenheit‚ selectable via a mode button․
Important indicators often include a low battery symbol‚ alerting you to replace the batteries for continued accurate performance․
A scanning indicator‚ frequently represented by a small icon‚ shows when the thermometer is actively measuring․
Some models feature backlight functionality for visibility in low-light conditions‚ described within the manual․
Error codes‚ such as “Lo” or “Hi”‚ signal readings outside the measurement range‚ requiring troubleshooting as outlined in the PDF․
The manual will also explain any specific symbols related to emissivity settings or other advanced features․
Understanding these indicators is vital for interpreting results correctly and ensuring reliable temperature assessment․
Buttons & Functions
Your infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF details the specific functions of each button‚ crucial for proper operation․
The power button‚ often prominently located‚ turns the device on and off‚ conserving battery life when not in use․
A measurement button initiates the temperature reading process; pressing and holding may be required for continuous scanning․
The mode button typically allows switching between temperature units (°C/°F) and potentially other settings like emissivity․
Some models include an up/down button for navigating menus or adjusting settings as described in the PDF․
A light button activates the backlight for improved visibility in dimly lit environments․
The manual will illustrate button locations and explain any combination presses needed for advanced features․
Familiarizing yourself with these controls‚ as outlined in the instruction manual PDF‚ ensures accurate and efficient temperature measurements․
Battery Compartment
The infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF provides detailed guidance on battery installation and replacement․
Typically located on the device’s handle or back‚ the battery compartment houses the power source‚ usually AAA or AA batteries․
The PDF will illustrate the correct battery polarity (+ and -) to ensure proper functionality; incorrect insertion can damage the device․
Always use fresh batteries of the specified type‚ as mixing old and new batteries or using different types can lead to inaccurate readings․
The manual may also detail low-battery indicators and troubleshooting steps if the thermometer fails to power on․
Exercise caution when opening and closing the compartment to avoid damaging the battery door or internal components․
Refer to the instruction manual PDF for specific instructions regarding battery disposal and environmental considerations․
Proper battery maintenance‚ as described in the PDF‚ extends the thermometer’s lifespan and ensures reliable performance․

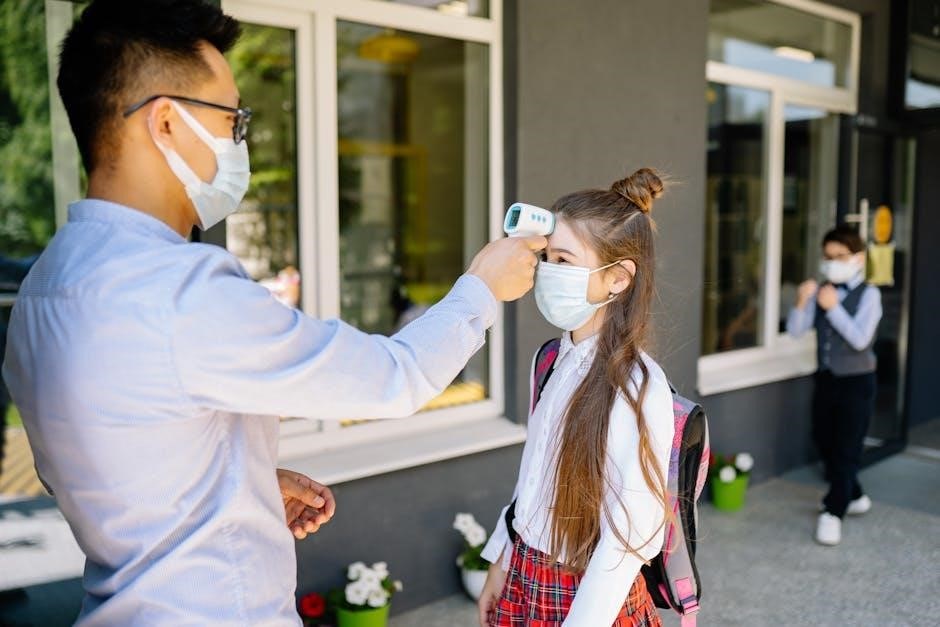
Operating Instructions
Consult the infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF for precise steps on powering the device‚ taking measurements‚ and switching between Celsius and Fahrenheit scales․
Powering On/Off
Powering On: Refer to your infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF to locate the power button‚ typically marked with a universal power symbol․ A firm‚ yet gentle‚ press will activate the device‚ initiating a self-test sequence displayed on the screen․ Ensure the battery is correctly installed for proper functionality‚ as detailed within the manual․ The display should illuminate‚ indicating the thermometer is ready for use․
Powering Off: To conserve battery life‚ always power off the thermometer after each use․ Again‚ consult the instruction manual PDF for the specific procedure․ Usually‚ a prolonged press of the power button will deactivate the device․ Some models feature an auto-shutoff function after a period of inactivity‚ a feature explained in the manual․ Proper shutdown prevents accidental readings and extends battery lifespan․ Always remove batteries for prolonged storage․
Taking a Temperature Measurement
Before initiating a measurement‚ carefully review the “Operating Instructions” section within your infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF․ Ensure the lens is clean and unobstructed for accurate readings․ For forehead thermometers‚ position the device at the recommended distance (typically 1-5cm) as specified in the manual․ For ear thermometers‚ gently insert the probe into the ear canal‚ following the guidelines detailed in the instruction manual PDF․
Press the measurement button and hold steady until a beep or visual indicator signals completion․ The temperature will then display on the screen․ The instruction manual PDF will outline specific techniques for optimal accuracy‚ including avoiding direct sunlight or drafts․ Always refer to the manual for proper usage and interpretation of results․
Switching Between Measurement Units (°C/°F)
Most infrared thermometers allow users to toggle between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) scales․ Consult your device’s infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF to locate the dedicated unit-switching button – often labeled “°C/°F” or a similar icon․ Typically‚ a single press of this button will cycle the display to the desired unit․
The instruction manual PDF may also detail alternative methods‚ such as holding the button for a specified duration․ Confirm the change by observing the unit symbol on the display screen․ It’s crucial to understand the selected unit when interpreting temperature readings․ Always refer to the instruction manual PDF for precise instructions specific to your model‚ ensuring accurate temperature conversions and consistent monitoring․

Interpreting Results & Troubleshooting
Interpreting readings requires understanding normal temperature ranges‚ detailed in your infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF․
Troubleshooting involves checking error codes and addressing factors impacting accuracy‚ as outlined within the manual․
Normal Temperature Ranges
Understanding normal temperature ranges is vital for accurate interpretation‚ and your infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF provides specific guidance․ Generally‚ a normal oral temperature is considered to be 97․6°F to 99․6°F (36․4°C to 37․6°C)․ However‚ ranges can vary slightly depending on the measurement site․
Forehead temperatures are typically a bit lower‚ around 96․8°F to 98․6°F (36°C to 37°C)․ Ear (tympanic) temperatures often read slightly higher‚ approximately 98․6°F to 100․4°F (37°C to 38°C)․ It’s crucial to consult the manual for the specific ranges applicable to your thermometer model․
A temperature of 100․4°F (38°C) or higher generally indicates a fever․ However‚ remember that individual baselines differ․ The manual will also detail how to account for environmental factors and proper usage to ensure reliable results․ Always refer to a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment․
Error Codes & Solutions
Your infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF details specific error codes and their corresponding solutions․ Common codes include “Lo” or “LL” indicating a low battery – replace batteries immediately․ An “Hi” or “HH” code signifies a temperature reading exceeding the thermometer’s range; allow the device to cool or measure a different object․
“Err” or a flashing display often suggests a sensor malfunction or improper operation․ Ensure the lens is clean and unobstructed‚ and that you’re following the correct measurement distance outlined in the manual․ If the error persists‚ try restarting the thermometer․
Some models display codes related to ambient temperature; refer to the manual for acceptable operating conditions․ Always consult the troubleshooting section of the PDF for a comprehensive list and detailed steps․ If issues remain unresolved‚ contact the manufacturer’s customer support․
Factors Affecting Accuracy
The infrared thermometer instruction manual PDF emphasizes several factors impacting accuracy․ Emissivity‚ the object’s ability to radiate infrared energy‚ is crucial; surfaces with varying emissivity require adjustments (some thermometers allow emissivity settings)․ Ambient temperature significantly influences readings – ensure the thermometer has acclimated to the surrounding environment before use․
Distance to the target is critical; maintain the recommended distance specified in the manual for optimal results․ Obstructions like dust‚ smoke‚ or reflective surfaces can distort measurements․ Human body temperature can be affected by factors like perspiration‚ skin perfusion‚ and recent activity․
Proper technique‚ as detailed in the PDF‚ is essential․ Regularly calibrate the thermometer according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to maintain precision․ Ignoring these factors can lead to inaccurate temperature assessments․